OUR LOCATIONSCall to book (212) 604-1300
OUR LOCATIONSCall to book (212) 604-1300
 OUR LOCATIONSCall to book (212) 604-1300
OUR LOCATIONSCall to book (212) 604-1300
Headaches, when combined with dizziness, fatigue, and neck pain, can have debilitating effects on your body. There is an entire spectrum of effects that affect the physical and mental health of a patient suffering from these conditions. There are several medical explanations for experiencing these conditions simultaneously.
So what are the causes and treatments for headache, dizziness, and fatigue caused by neck pain? Neck pain by itself could point to a musculoskeletal injury. However, when the patient experiences headaches and dizziness, it could imply a serious underlying condition. They include migraines, dehydration, or tumors. Some treatments for this include topical, medical, and surgical procedures, as well as some lifestyle changes and maintenance medications.
The problem with diagnosing patients suffering from headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and neck pain is the fact that there are numerous potential diseases that could manifest themselves through these symptoms. As such, treatment options heavily depend upon the diagnosis but can usually be managed with physical therapy. Here are some of the most common causes of these symptoms:
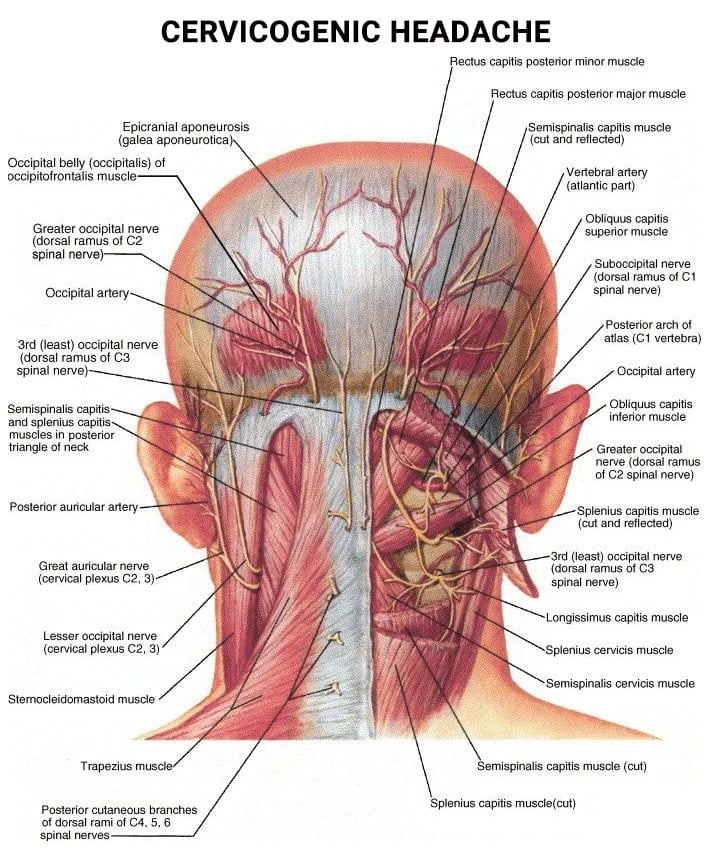
A cervical headache(also known as cervicogenic dizziness or headache) is a type of chronic headache that occurs due to structural problems with parts of the cervical spine such as the disc, vertebrae, muscle, or spinal cord. The part of the spine that houses the neck region is known as the cervical spine. Severe symptoms include neck pain, cervicogenic dizziness, fatigue, and cervical vertigo, along with headaches. Cervical spine damage can be a result of:
A cervical headache may cause prolonged pain and discomfort for several days. The condition may return at random times in the future. Other symptoms include increased blood pressure, nausea, restricted neck movement, neck stiffness, and exhaustion.
Doctors will diagnose cervical headaches by closely examining the neck to determine the damage the spine has incurred using medical imaging techniques. While treatment options depend on the severity of the cervicogenic dizziness and the cause of the headache, there are a few viable options that your doctor might recommend. These include:
A moderate to severe headache that only affects one side of the brain is known as a migraine. Additional symptoms of a migraine headache include heightened sensitivity to stimuli, high blood pressure, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting could also result from them. Health professionals have a variety of hypotheses on what causes migraines. These include:
Migraines are actually common amongst the population, and it can cause extreme discomfort to the patient. There is no definitive cure for a migraine, but there are some treatment solutions that your doctor might recommend to reduce the symptoms. These include:
The term “gastroenteritis” refers to the medical condition of intestinal inflammation and irritation. Inflammation brought on by a virus is known as viral gastroenteritis (VG). The most typical of them is the norovirus, which can result in a variety of symptoms, such as:
Without medical intervention, viral gastroenteritis typically resolves on its own. People can control their diarrhea and symptoms by taking medication. Loperamide (Imodium) and bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto Bismol) are common examples of medicines for VG. The best way to prevent viral gastroenteritis is to stay hydrated, avoid dehydration, and replace lost electrolytes by consuming low-sugar fruit juices or sports drinks.
A swollen blood vessel is referred to as an aneurysm. This happens as a result of a blood vessel wall weakening. A cerebral aneurysm is an aneurysm that develops within a blood artery in the brain. It’s possible that a minor brain aneurysm that doesn’t become larger presents with no symptoms. Larger aneurysms, however, may exert pressure on the nearby nerves or brain tissue, resulting in the symptoms listed below:
An aneurysm may occasionally rupture or leak, necessitating immediate medical care. A developing cerebral aneurysm is clearly indicated by a sudden, severe, and intense headache. Other signs to watch out for are:
Most doctors and experts are in consensus that most aneurysms don’t require treatment. Your medical provider will most likely wish to monitor the growth of the aneurysm to ensure that it doesn’t progress or rupture. Monitoring blood pressure, quitting smoking, and avoiding intake of stimulant drugs, are reliable ways to reduce the risk of an aneurysm rupturing. Surgery may be required in some cases to cut off blood supply to the aneurysm.
A stroke is a potentially fatal disorder in which the blood supply to a portion of the brain is interrupted, which may cause the death of brain cells. A sudden and intense headache is a common symptom of a stroke. A clogged artery that provides blood to the brain or a burst blood vessel inside the brain can both cause a stroke. Other signs of a stroke besides a headache include:
Strokes are usually a medical emergency that could cause fatal brain damage or result in death. If at all possible, a person who exhibits symptoms of a stroke should call for an ambulance right away. Those who suspect a stroke should be on the lookout for these signs in others and seek immediate medical attention. The following are possible treatment options:
When a group of cells within the brain multiply improperly and uncontrollably, the result is a brain tumor. According to how quickly they develop and how likely they are to come back after therapy, doctors assign brain tumors a grade. Brain tumors in grades 1 and 2 are benign or noncancerous and grow slowly. Brain tumors in grades 3 and 4 are cancerous or malignant.
It’s possible for these tumors to develop in the brain or to spread from another part of the body. They spread quickly and are more likely to return after therapy. The symptoms of a brain tumor are somewhat influenced by the portion of the brain they impact. Some typical signs include:
The course of treatment to be taken for a patient with a brain tumor is determined by a number of factors and variables. The type, location, and grade of the tumor is perhaps the most significant factor. Other factors are the level of abnormality of the cancerous cells, size of the tumor, the extent of lesions, and overall health of the patient. Possible treatment options include:
People may also experience headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and neck pain if their body is dehydrated. Dehydration occurs when the body doesn’t have enough water in its system to function properly. Concerning symptoms also include a dry mouth, dry lips, and eyes.
Urine may also have a characteristic strong stench, and there may also be a reduced urine output. Hydrating by drinking plenty of water and electrolytes while taking a few days of rest should help restore your body’s fluid levels.
Headaches are a common side-effect of anxiety. People suffering from anxiety may also have an elevated heart rate and may experience panic attacks. These panic attacks usually have the following symptoms:
There are certain general treatment techniques that can be recommended to minimize the effects of headache, dizziness, fatigue, and neck pain. Physical therapy is a great way to help regain motor functions, especially after suffering from chronic neck pain, a cerebral aneurysm, or a cervical headache. Acupuncture therapy has also shown promising results. Other treatment techniques include:
There are several preventive measures and treatment options that are specific to different conditions. Headaches caused by tension can be reduced by taking OTC pain medication and getting massages. Managing stress, eating meals regularly, getting adequate rest, regular exercise, and staying hydrated are common preventive measures for headaches.
Cervicogenic headaches can be treated by using nerve blockers in the upper cervical spine, undergoing physical therapy for neck muscles, and taking pain medicine for neck pain. Pain relievers, stress management strategies, hormone therapy, and drinking an adequate amount of fluids can help prevent migraine attacks. Other general preventive measures include:
Anyone experiencing severe, ongoing, or escalating headaches should consult a physician for a diagnosis. A series of headaches with abnormal symptoms that have only been occurring recently might be a cause for concern. If you experience fever, nausea, persistent vomiting, and a stiff neck, then your system may have an underlying issue that needs urgent medical attention.
Mood changes, confusion, personality changes, behavioral changes, loss of consciousness, blackouts, seizures, and a foggy memory point to a neurological disorder that would require a medical expert’s opinion. Consult with your doctor immediately if you have had a prior history of headaches that have progressively gotten worse over time.
Headaches and neck pain can impact your ability to go on with your day-to-day life. It can even deprive you of a good night’s sleep over long periods of time. Dizziness and fatigue can further complicate these issues. Getting a medical professional to have a look at your condition to diagnose the exact cause of your symptoms is the best way to get yourself back to optimum health.
Our expert team of pain physicians at New York Pain Care is trained in a variety of surgical and non-surgical treatments to relieve pain. The source of your headaches will be accurately identified and addressed head-on to help you return to a pain-free life. Say goodbye to body pain and contact us today.