OUR LOCATIONSCall to book (212) 604-1300
OUR LOCATIONSCall to book (212) 604-1300
 OUR LOCATIONSCall to book (212) 604-1300
OUR LOCATIONSCall to book (212) 604-1300

Back pains are quite common because there are a plethora of possible reasons why they happen – from simple ones like stress or more serious diseases, such as herniated discs or scoliosis. The same goes for stomach aches – they may be caused by overeating or autoimmune disorders. But if the co-occurrence of these symptoms happens too often, it’s time to consult a doctor to find out the exact reason.
So why do the upper stomach and back feel painful at the same time? These two uncomfortable symptoms are causes for concern because they might be a sign of more serious health conditions like pancreatitis, kidney stones, peptic ulcer, and gallstones.
Got stomach and back pains? These two symptoms are quite common among Americans. Back pains are the most common reason why employees call in sick at work. While they’re both extremely uncomfortable, stomach and back pains happening at the same time are a cause for concern. It usually means that there is a problem with the internal organs located in the area.
Here are some of the possible causes of upper stomach and back pain:
The pancreas is the large gland found in the abdomen – behind the stomach and next to the small intestines. It’s important for producing digestive enzymes that break down the food and help the body digest it. It also releases insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to assist the body in converting food into energy.
When the pancreas gets inflamed, pancreatitis occurs. The organ is damaged when the enzymes start working while they’re still in the pancreas. The two kinds of pancreatitis are:
The main cause of acute pancreatitis remains unknown for some patients, but here are some of the possible causes:
On the other hand, chronic pancreatitis is more common for people aged between 30 to 40. It shares the same possible causes with acute pancreatitis in addition to the following:
Aside from recurring back and abdominal pain, pancreatitis is also accompanied by the following symptoms:
The doctor examines the blood to check if the levels of lipase and amylase are high. This helps them determine if the patient has acute pancreatitis. They might also perform other tests including:
Acute pancreatitis patients are advised to stay in the hospital for a few days so the doctor may easily monitor their condition. They prescribe antibiotics to treat the infected pancreas. Patients are also given intravenous fluid through a needle and pain medications. They’re also put under a low-fat diet until the pancreas fully recovers. For more severe cases, ERCP, Gallbladder surgery, or pancreas surgery might be necessary.
As for chronic pancreatitis patients, they might need to stay in the hospital longer and undergo more procedures. Some of the treatments include insulin injections, pain medicines, pancreatic enzymes, and surgery to relieve pain and treat blockages.
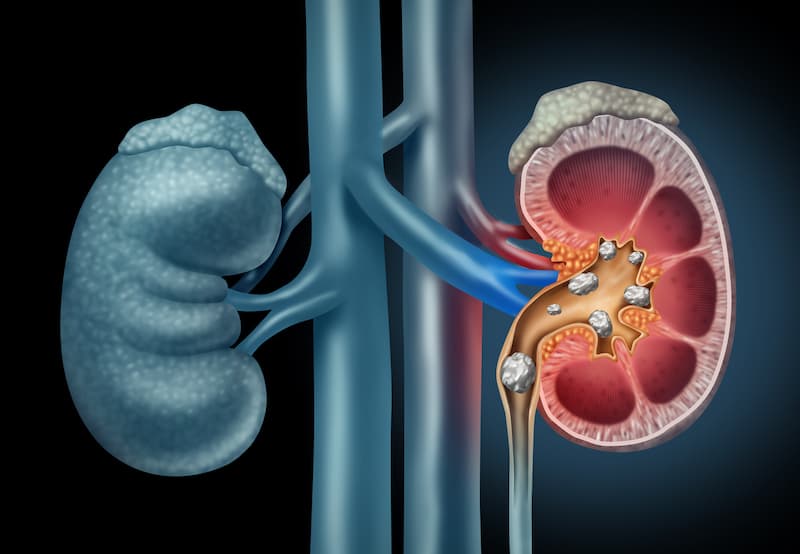
Kidney stones refer to the hard objects that develop inside the kidneys. They’re generally made of salts and minerals that are about the size of a grain of sand to a corn kernel. They usually cause back pain that travels to the upper abdominal area on the side of the affected kidney.
Kidney stones form when the urine has a high mineral concentration accompanied by other substances, such as uric acid, oxalate, and calcium. These substances react and form tiny crystals that stick together until they form stones. The lack of water or other fluids in the body to dilute these materials is also another reason why these stones form.
Kidney stones might be as small as sand grains, but they might also become as big as corn kernels. Bigger stones block the urine flow and are painful to pass. The formation of kidney stones depends on a person’s diet and the medications they take. There’s also a huge chance that a person has kidney stones if someone else in their family has had them before.
Most patients don’t feel any symptoms unless the stones start moving inside the kidneys down to the ureter. During this time, the pain shifts to wherever the kidney stones are. Other symptoms of kidney stones include:
Kidney stones may affect anyone, so it’s crucial to know more about their symptoms. The best way for an individual to know if they have kidney stones is to consult a physician. They’re usually asked to describe the intensity and frequency of the symptoms. Doctors also ask about medications or vitamins that the patient takes. They might also perform any of the following tests:
Kidney stones pass on their own without causing long-term detrimental effects on the body. However, kidney stones that remain in the body for a long time might cause kidney infection.
If the patient is in a lot of pain because the stones are too big, the doctor might recommend surgery to remove the stones or break them down. Here are some of the procedures to eliminate kidney stones through surgery:

Peptic ulcer refers to the presence of open sores on the stomach’s lining and upper area of the small intestines. This happens when the stomach acids slowly strip the digestive tract’s protective mucus layer. Some patients might not experience symptoms, but others feel upper stomach pain or lower abdominal pain.
A peptic ulcer might lead to internal bleeding, which is why early diagnosis is crucial. There are two types of peptic ulcer:
Ulcers occur in people of all ages, but older people have higher risks of developing this condition. There are two major causes of peptic ulcer:
Small ulcers don’t cause symptoms. But if a person starts feeling a burning pain between their breastbone and belly button, it’s time to consult a physician. Antacids are enough to relieve pain for some time, but it usually returns. Other symptoms of peptic ulcer include:
During the consultation with the doctor, the patient is asked about the symptoms, medical history, and medications. The physician also examines the belly for abdominal bloating and pain. These are usually enough to diagnose a peptic ulcer, but further examinations might be needed for some cases.
The best way to confirm if the patient has a peptic ulcer is through X-rays or endoscopy. The doctor inserts a thin tube down the throat to check the stomach and small intestines for ulcers. They might also take a sample of the lining to check for bacteria.
Peptic ulcers might heal on their own. However, they usually return if not treated properly. After determining the cause of ulcers, the doctor may either prescribe antibiotics or ask the patient to limit their NSAIDs intake. Antacids and pain relievers might also be recommended to help with the severe pain.
The gallbladder is the small organ found under the liver. It’s responsible for storing and releasing bile that’s important for digestion. This liquid carries cholesterol and bilirubin, the byproduct of red blood cells when the body breaks them down. These wastes are responsible for the formation of gallstones in the gallbladder.
The size of the gallbladder can be as small as sand grains to as big as golf balls. It’s difficult to know if a person has gallstones unless they start blocking the bile duct and causing back and stomach pains.
Gallstones start forming in the body under either of these three conditions:
Gallstones are usually asymptomatic until they start blocking the bile duct. Aside from upper abdominal pain, the patient might also experience:
The condition might be severe if the patient starts experiencing:
Aside from a physical examination, the physician might also perform the following tests:
Smaller gallstones typically pass through the body on their own, which is why treatment isn’t necessary for asymptomatic patients. People diagnosed with gallstones usually have their entire gallbladders removed through:
If the gallstones are found in the bile duct, the doctor performs ERCP to find and take them out. For cases that don’t require surgery, medications are enough to dissolve the stones.
The back is a support and stabilizing system for the body, which is why it’s easily affected by different symptoms including severe stomach pain. Aside from pancreatitis, kidney stones, gallstones, and peptic ulcer, there are other reasons for recurring stomach ache and back pain.
Finding out the exact cause of the abdominal and back pain gives a person long-lasting relief. There are different methods to treat the exact condition, but here are some of the best home remedies to reduce severe abdominal pain and upper back discomfort:
NYPC is home to board-certified doctors and best pain management specialists in New York. Our highly trained team is here to provide non-surgical treatments to many conditions that cause extreme pain and discomfort to our clients in NYC and NJ.
Take the first step to a pain-free life with us today. Visit our website to try out our pain assessment tool or contact us at (646) 846-1824 to book an appointment.
Learn more: Upper Back Pain During Pregnancy